Please review the HAZOP Tutorial if you have not already done so.
Results
Great job!
Please review the HAZOP Tutorial on the SAFEChE Process Safety Website.
#1. What is the purpose of a HAZOP? ? Select one answer
INCORRECT!
A Hazard and Operability Study, commonly referred to as a HAZOP study, is a structured analysis in process design to identify potential process safety incidents that a facility is vulnerable to. A HAZOP study uses guide words to systematically determine possible failures that could result from operation of equipment outside of design conditions. This out of design condition can occur due to possible mal-operation or mal-function of individual items of equipment, instruments, or control system.
HAZOP studies are routinely performed on:
- New plants where the design is nearly firm and documented
- Existing plants as a part of a periodic hazard analysis or a management of change process
#2. Which of the following causes are considered in a HAZOP study?
Select all that apply:
INCORRECT!
While completing a HAZOP, please consider the following:
- Failure of pressure safety valves/rupture discs are Not taken as a cause due to them being the last layer of defense. Pressure safety valves shall be considered as a safeguard.
- Design related issues are Not considered as a cause because it is assumed that design calculations are correct. (e.g. incorrect line sizes in original designs)
- It is assumed that all the equipment and control systems are working as per design intent. (e.g. we don’t take incorrect pressure setpoints of relief valve)
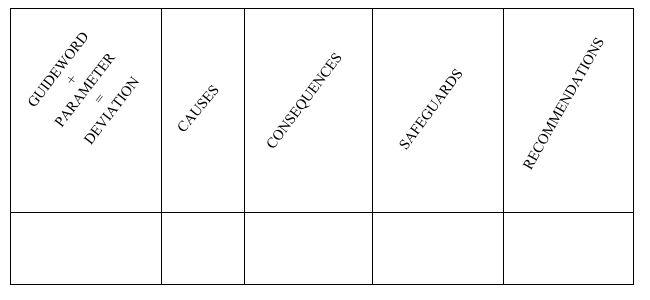
- In the case of multiple units of equipment (e.g. valves/Reboiler/Pumps), ensure to mention the equipment name defined in the figure (e.g. Valve X1, pump Y1) for clarification.
- It is also possible that there is no safeguard present for a system. In this case, specify “None” in “Safeguard” column.
- Standby equipment (pumps, reboilers etc.) can be considered as safeguards in the event of failure of existing equipment. This is because standby equipment can be taken inline to prevent any economic penalty or hazardous situation.
- One “Deviation” can be a cause of another “Deviation” (e.g. More flow can be a cause of More level)
- A protection system can be a cause and a safeguard for different cases. (e.g. level transmitter failure can be a cause for high level, but a level transmitter can act as safeguard in case of more flow)
- Specify only those causes which can independently lead to a “Deviation” (e.g. a closed tank outlet valve and more inlet flow can independently lead to high tank level)
- Standard Operating Procedure, if available, can be taken as safeguard when there is manual operation.
- Do not consider cases where two unrelated/independent causes can simultaneously occur
Note: Following causes are not considered in HAZOP study:
- Simultaneous occurring of two unrelated incidents is not considered due to very low probability (e.g. more reactant level and failure of cooling jacket in a reactor)
- Simultaneous failure of more than one independent protection devices is not considered due to low probability (e.g. simultaneous failure of high-level alarm and overfill protection system)
- Natural Calamity (e.g. Earthquake, Flood, Cyclones etc.)
- Sabotage
#3. Which of the following are examples of guide words?
Select all that apply:
INCORRECT!
A list of HAZOP Guide Words can be found in Table 1 below.
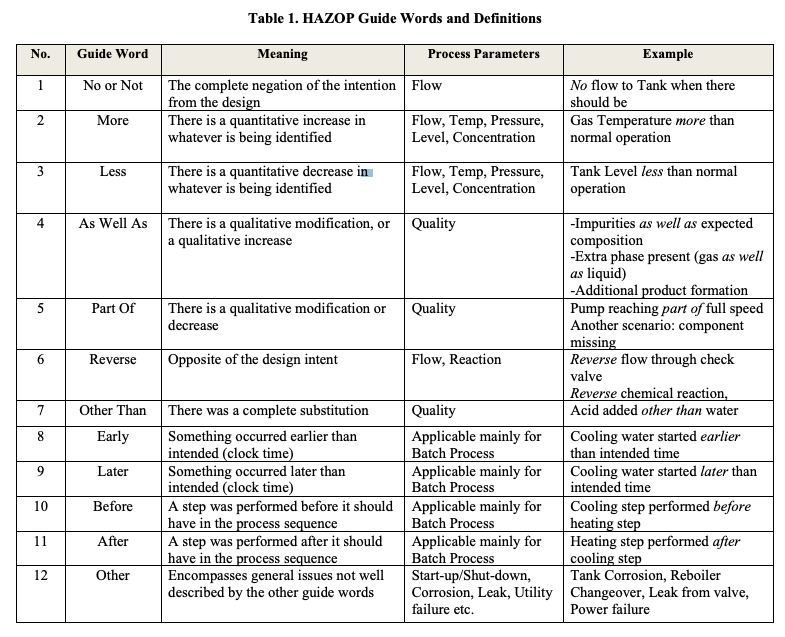
#4. Which of the following are examples of process parameters?
INCORRECT!
Temperature, Pressure, Flow Rate, and Level are ALL considered to be process parameters.
Other process parameters may include pH, concentration, viscosity, volume, etc.




