Prepared in collaboration with Kara Steshetz, Ayush Agarwal and Marina Miletic
Introduction
The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the importance of carefully analyzing hazards in a process in order to implement effective preventative and mitigation barriers. A BowTie diagram is a form of risk assessment to identify these potential hazards. It is a visualization of the path a hazard may take “to cause a severe consequence and the combination of preventative and mitigative barriers … required to reduce the process safety risk” (Vaughen & Bloch, 2016). It can be applied to many fields and situations, not strictly chemical engineering.
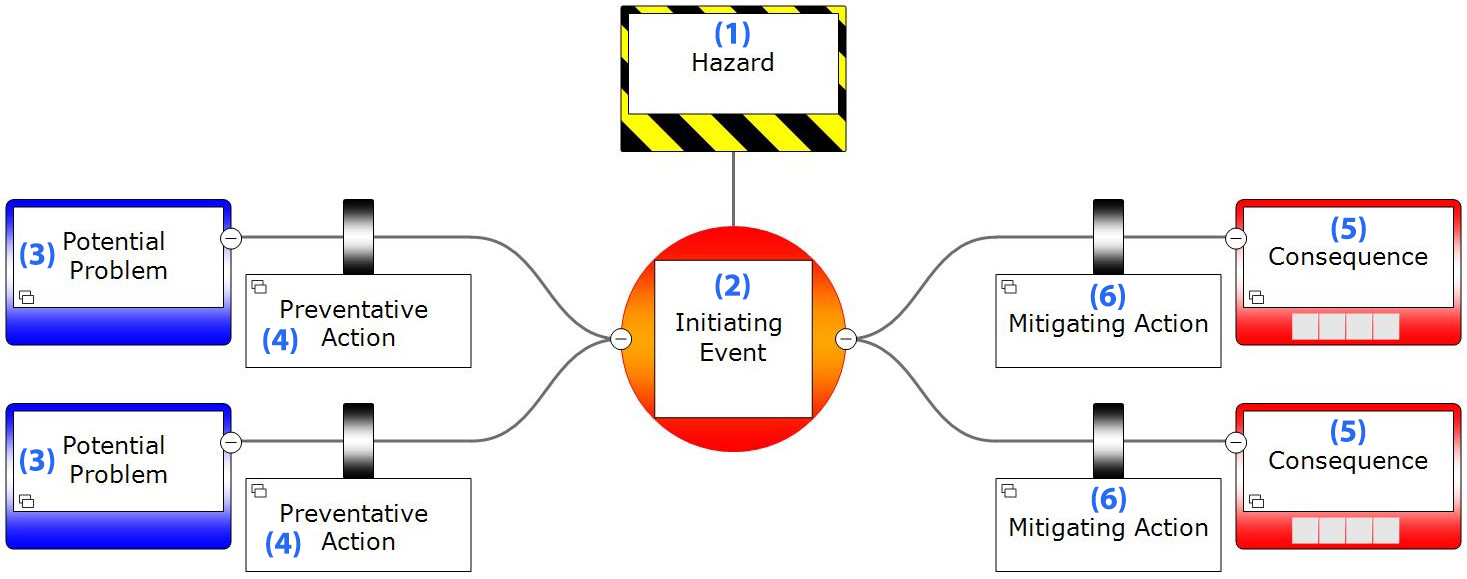
Below is the general BowTie diagram. Click on each section for a description of each element.
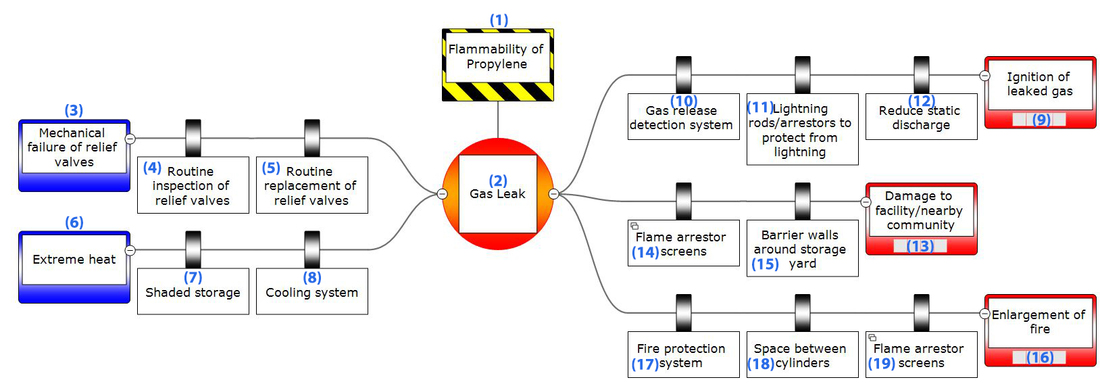
Example: Incident at Praxair
On June 24, 2005 in St. Louis, MO, summer temperatures reached 96 ᵒF. Praxair stored propylene gas cylinders outside in a storage yard on top of asphalt. The vapor pressure in the cylinders exceeded faulty set pressures of the relief valves allowing propylene to vent into the storage yard area. The resulting vapor plume was ignited by a static discharge. The fire enlarged when other cylinders began to vent and eventually cylinders began to explode. There was significant damage to the facility and the surrounding community. (CSB Praxair video / CSB Praxair incident report)
Below is the BowTie diagram for the Praxair facility. Click on each section for a description of each element.
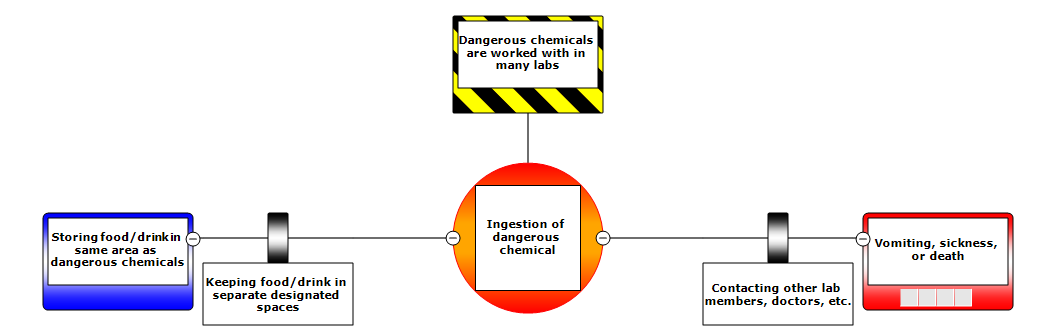
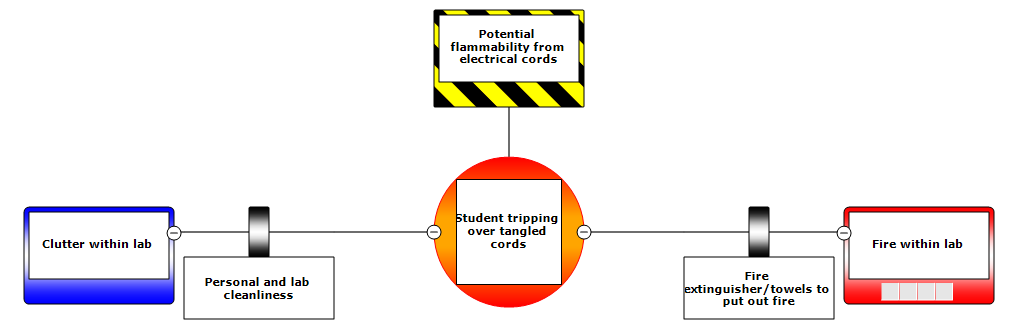
Other Examples
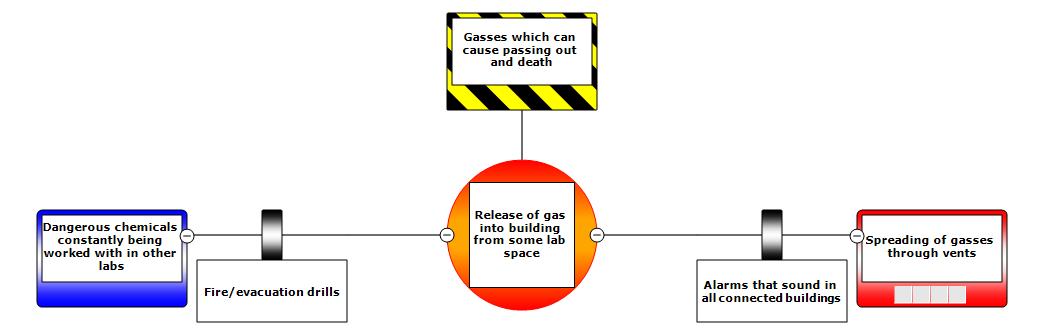
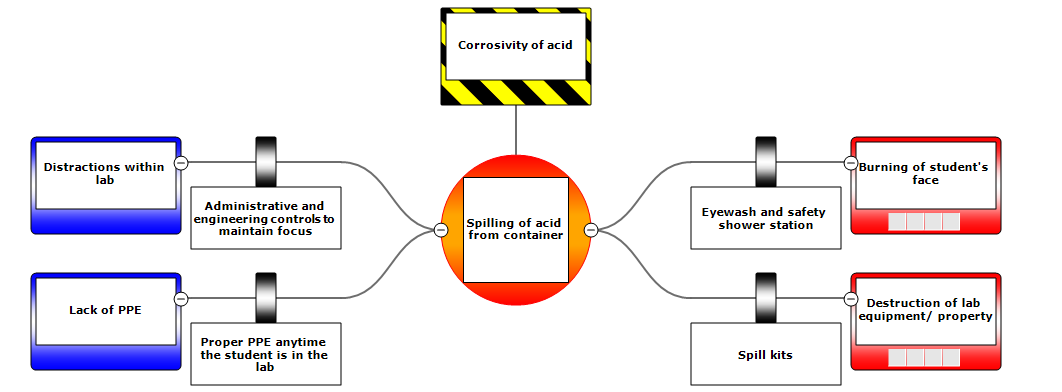
Below are some examples of BowTie diagram. Click on each section for a description of each element.
These BowTie Example are based on lab safety videos produced by University of Michigan’s EECS department. The videos (in order of the BowTie Examples below) are:
Critical Thinking
- What other preventative barriers could be put in place to increase the effectiveness of the safety measures in this scenario?
- What other mitigating barriers could be put in place to decrease the escalation to one or more of the consequences in this scenario?
- What other chemical or operational hazards are present in this scenario?
- What are some practices, programs, or management systems Praxair could implement that would be effective in managing these other hazards?
Knowledge Check
There is a Bow Tie Model knowledge check quiz available.
References
- U.S. Chemical Safety Board. Fire at Praxair St. Louis: Dangers of Propylene Cylinders. Washington DC, 2006. https://www.csb.gov/praxair-flammable-gas-cylinder-fire/
- Hatch, D., McCulloch, P., & Travers, I. (2017, November). Visual HAZOP. The Chemical Engineer(917), 27-32.
- The Bowtie Method. (2018). Retrieved from Patient Safety BowTies. http://www.patientsafetybowties.com/knowledge-base/6-the-bowtie-method#Top%20event
- U.S. Chemical Safety Board. “CSB Safety Video: Dangers of Propylene Cylinders.” Online video clip. YouTube, 10 October 2007. Web. 8 May 2018.
- Vaughen, B. K., & Bloch, K. (2016, December). Use the Bow Tie Diagram to Help Reduce Process Safety Risks. Chemical Engineering Progress, 30-36.
